Depression and substance use disorders are often co-occurring conditions, with each condition influencing the other in a complex and detrimental way. This article delves into the intricate relationship between these two disorders, exploring their causes, consequences, and treatment approaches.
Depression can lead to substance use as a form of self-medication, while substance use can worsen the symptoms of depression and interfere with treatment. Understanding the interplay between these disorders is crucial for developing effective interventions and improving outcomes for individuals struggling with both conditions.
Depression and Substance Use Disorders: A Complex Interplay
Depression and substance use disorders are often intertwined, with one condition exacerbating the other. Understanding the co-occurrence of these disorders is crucial for effective treatment and prevention.
Co-occurrence of Depression and Substance Use Disorders
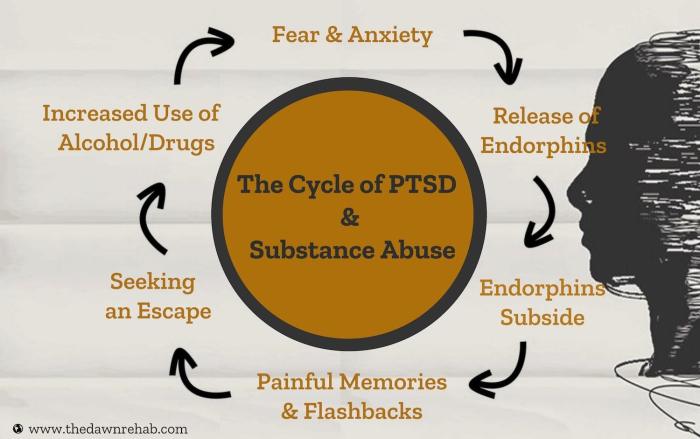
Depression and substance use disorders frequently co-occur, with a significant overlap in symptoms and risk factors. This co-occurrence can lead to more severe and treatment-resistant conditions.
- Genetic Factors:Shared genetic vulnerabilities contribute to both depression and substance use disorders, increasing the likelihood of co-occurrence.
- Environmental Factors:Adverse childhood experiences, such as trauma or neglect, can increase the risk of both conditions.
- Psychological Factors:Individuals with depression may turn to substances as a form of self-medication, seeking relief from negative emotions.
Impact of Depression on Substance Use
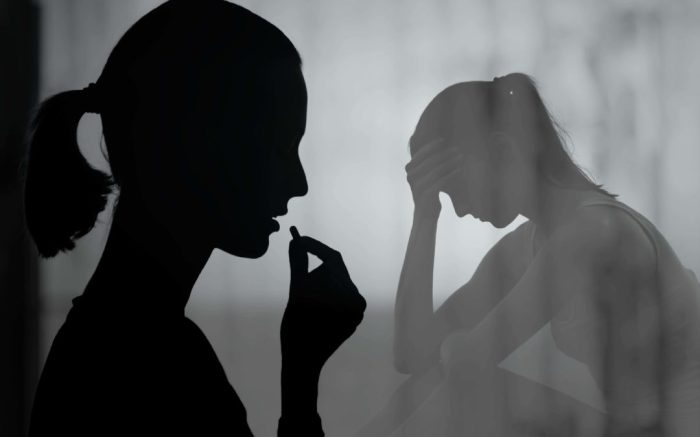

Depression can drive individuals to use substances as a coping mechanism, leading to a vicious cycle.
- Self-Medication:Substances can provide temporary relief from depressive symptoms, leading to a false sense of well-being.
- Increased Vulnerability:Depression can impair decision-making and self-control, making individuals more susceptible to substance use.
- Exacerbation of Substance Use Disorders:Depression can worsen the severity of substance use disorders, increasing the risk of relapse and overdose.
Impact of Substance Use on Depression
Substance use can worsen depressive symptoms and interfere with treatment.
- Worsening of Symptoms:Substances can disrupt neurotransmitter balance, exacerbating depressive symptoms and making them more resistant to treatment.
- Interference with Treatment:Substance use can interfere with the efficacy of antidepressants and therapy, reducing the likelihood of successful recovery from depression.
- Increased Risk of Suicide:The combination of depression and substance use significantly increases the risk of suicide.
Treatment Considerations for Co-occurring Disorders
Treating co-occurring depression and substance use disorders requires an integrated approach that addresses both conditions simultaneously.
- Integrated Treatment:Comprehensive treatment plans involve a combination of psychotherapy, medication, and support services tailored to the individual’s needs.
- Sequential Treatment:In some cases, sequential treatment may be necessary, where one condition is prioritized over the other based on severity and prognosis.
- Challenges:Treating co-occurring disorders is complex and challenging, requiring collaboration between mental health and addiction specialists.
Prevention and Early Intervention
Preventing and addressing co-occurring depression and substance use disorders requires a multi-faceted approach.
- Early Intervention:Screening for both depression and substance use is crucial, particularly in high-risk populations.
- Prevention Programs:Education and awareness programs aimed at reducing stigma and promoting healthy coping mechanisms can help prevent the onset of both conditions.
- Community Support:Strong community support systems and access to mental health and addiction services are essential for early detection and intervention.
End of Discussion: Depression And Substance Use Disorders

Addressing the co-occurrence of depression and substance use disorders requires a comprehensive approach that integrates mental health and addiction treatment services. Early intervention and prevention strategies are essential to reduce the burden of these disorders and promote the well-being of individuals and communities.
Commonly Asked Questions
What are the common factors that contribute to the co-occurrence of depression and substance use disorders?
Genetic, environmental, and psychological factors can all play a role in the development of both depression and substance use disorders.
How does depression affect substance use?
Depression can lead to substance use as a form of self-medication, to alleviate symptoms such as sadness, anxiety, and insomnia.
How does substance use affect depression?
Substance use can worsen the symptoms of depression, interfere with treatment, and increase the risk of relapse.
What are the challenges in treating co-occurring depression and substance use disorders?
Treating co-occurring disorders requires a comprehensive approach that addresses both conditions simultaneously. Challenges include the high prevalence of relapse, the need for specialized treatment programs, and the stigma associated with both disorders.